Distance from Velocity-Time Graph | Motion in 1D | JEE Physics | Doubtify JEE
📈 Velocity-Time Graph Problem | Motion in One Dimension | Physics | Doubtify JEE
💡 Question:
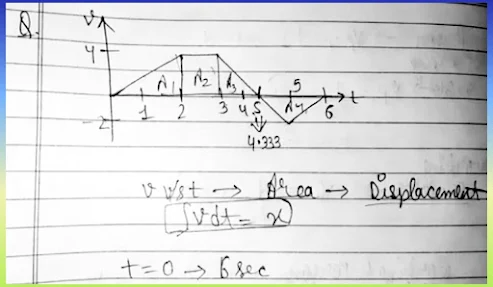
The velocity (v) and time (t) graph of a body in a straight-line motion is shown in the figure. Point S is at 4.333 sec. The total distance covered by the body in 6 seconds is?
🖼️ Question Image:
🧠 Solution Image:
✍️ Detailed Explanation:
To find the total distance, we analyze the area under the velocity-time graph. Remember, the area above the time axis (positive velocity) adds to distance, and the area below (negative velocity) also adds to distance—just as a positive value.
Step-by-step:
-
From 0 to 4.333 s (point S):
-
Velocity is positive.
-
Use the area of a triangle or trapezium, depending on the graph.
-
-
From 4.333 to 6 s:
-
If velocity is negative here, it implies a reversal in direction.
-
We still take the absolute value of the area for distance.
-
-
Total Distance = Area(0 to 4.333 s) + |Area(4.333 to 6 s)|
Use appropriate area formulas:
-
Triangle:
-
Trapezium:
🧠 Pro Tip:
Understanding how to interpret velocity-time graphs not only helps in JEE but builds your intuition for real-world motion problems. Always look for turning points (like where velocity becomes zero) as these can mark direction changes.
🎥 Video Solution:
🔍 Why this Question is Important:
-
Tests core concepts of kinematics and graphical analysis.
-
Helps students visualize motion instead of memorizing formulas.
-
Common in JEE Mains and school-level Physics exams.
-
Distinguishes between distance and displacement.
📩 Have a Doubt?
DM us on Instagram @doubtifyJEE or email at doubtifyqueries@gmail.com — We're always here to help you out!







Comments
Post a Comment
Have a doubt? Drop it below and we'll help you out!